2021
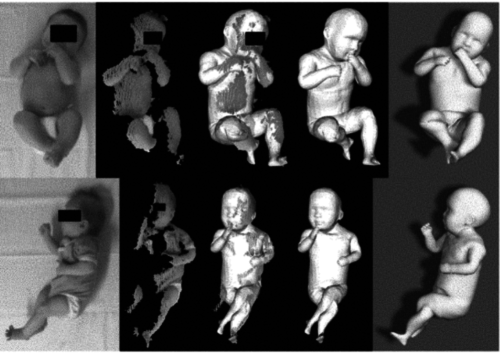
Skinned multi-infant linear body model
Hesse, N., Pujades, S., Romero, J., Black, M.
(US Patent 11,127,163, 2021), September 2021 (patent)
2020
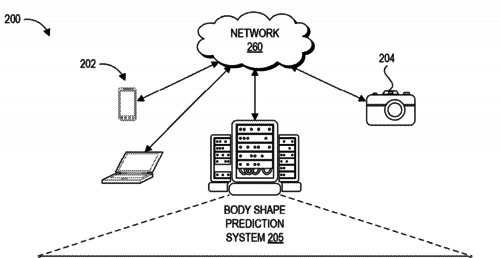
Machine learning systems and methods of estimating body shape from images
Black, M., Rachlin, E., Heron, N., Loper, M., Weiss, A., Hu, K., Hinkle, T., Kristiansen, M.
(US Patent 10,679,046), June 2020 (patent)
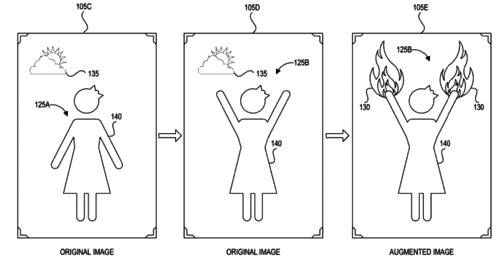
Machine learning systems and methods for augmenting images
Black, M., Rachlin, E., Lee, E., Heron, N., Loper, M., Weiss, A., Smith, D.
(US Patent 10,529,137 B1), January 2020 (patent)
2019
Method for providing a three dimensional body model
Loper, M., Mahmood, N., Black, M.
September 2019, U.S.~Patent 10,417,818 (patent)
2018
Method and Apparatus for Estimating Body Shape
Black, M. J., Balan, A., Weiss, A., Sigal, L., Loper, M., St Clair, T.
June 2018, U.S.~Patent 10,002,460 (patent)
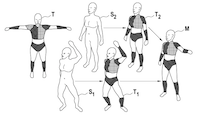
Co-Registration – Simultaneous Alignment and Modeling of Articulated 3D Shapes
Black, M., Hirshberg, D., Loper, M., Rachlin, E., Weiss, A.
February 2018, U.S.~Patent 9,898,848 (patent)
2017
Parameterized Model of 2D Articulated Human Shape
Black, M. J., Freifeld, O., Weiss, A., Loper, M., Guan, P.
September 2017, U.S.~Patent 9,761,060 (patent)
Crowdshaping Realistic 3D Avatars with Words
Streuber, S., Ramirez, M. Q., Black, M., Zuffi, S., O’Toole, A., Hill, M. Q., Hahn, C. A.
August 2017, Application PCT/EP2017/051954 (patent)
System and method for simulating realistic clothing
Decentralized Simultaneous Multi-target Exploration using a Connected Network of Multiple Robots
Nestmeyer, T., Robuffo Giordano, P., Bülthoff, H. H., Franchi, A.
In pages: 989-1011, Autonomous Robots, 2017 (incollection)
2016
Skinned multi-person linear model
Black, M.J., Loper, M., Mahmood, N., Pons-Moll, G., Romero, J.
December 2016, Application PCT/EP2016/064610 (patent)
2014
Advanced Structured Prediction
Nowozin, S., Gehler, P. V., Jancsary, J., Lampert, C. H.
Advanced Structured Prediction, pages: 432, Neural Information Processing Series, MIT Press, November 2014 (book)
Human Pose Estimation from Video and Inertial Sensors
Simulated Annealing
2013
Human Pose Calculation from Optical Flow Data
System and method for generating bilinear spatiotemporal basis models
Matthews, I. A. I. S. T. S. K. S. Y.
US Patent Application 13/425,369, March 2013 (patent)
Modeling Shapes with Higher-Order Graphs: Theory and Applications
Wang, C., Zeng, Y., Samaras, D., Paragios, N.
In Shape Perception in Human and Computer Vision: An Interdisciplinary Perspective, (Editors: Zygmunt Pizlo and Sven Dickinson), Springer, 2013 (incollection)
Class-Specific Hough Forests for Object Detection
Gall, J., Lempitsky, V.
In Decision Forests for Computer Vision and Medical Image Analysis, pages: 143-157, 11, (Editors: Criminisi, A. and Shotton, J.), Springer, 2013 (incollection)
Image Gradient Based Level Set Methods in 2D and 3D
Xianhua Xie, Si Yong Yeo, Majid Mirmehdi, Igor Sazonov, Perumal Nithiarasu
In Deformation Models: Tracking, Animation and Applications, pages: 101-120, 0, (Editors: Manuel González Hidalgo and Arnau Mir Torres and Javier Varona Gómez), Springer, 2013 (inbook)
2012
Exploiting pedestrian interaction via global optimization and social behaviors
Leal-Taixé, L., Pons-Moll, G., Rosenhahn, B.
In Theoretic Foundations of Computer Vision: Outdoor and Large-Scale Real-World Scene Analysis, Springer, April 2012 (incollection)
Data-driven Manifolds for Outdoor Motion Capture
Pons-Moll, G., Leal-Taix’e, L., Gall, J., Rosenhahn, B.
In Outdoor and Large-Scale Real-World Scene Analysis, 7474, pages: 305-328, LNCS, (Editors: Dellaert, Frank and Frahm, Jan-Michael and Pollefeys, Marc and Rosenhahn, Bodo and Leal-Taix’e, Laura), Springer, 2012 (incollection)
Scan-Based Flow Modelling in Human Upper Airways
Perumal Nithiarasu, Igor Sazonov, Si Yong Yeo
In Patient-Specific Modeling in Tomorrow’s Medicine, pages: 241 - 280, 0, (Editors: Amit Gefen), Springer, 2012 (inbook)
An Introduction to Random Forests for Multi-class Object Detection
Gall, J., Razavi, N., van Gool, L.
In Outdoor and Large-Scale Real-World Scene Analysis, 7474, pages: 243-263, LNCS, (Editors: Dellaert, Frank and Frahm, Jan-Michael and Pollefeys, Marc and Rosenhahn, Bodo and Leal-Taix’e, Laura), Springer, 2012 (incollection)
Home 3D body scans from noisy image and range data
Weiss, A., Hirshberg, D., Black, M. J.
In Consumer Depth Cameras for Computer Vision: Research Topics and Applications, pages: 99-118, 6, (Editors: Andrea Fossati and Juergen Gall and Helmut Grabner and Xiaofeng Ren and Kurt Konolige), Springer-Verlag, 2012 (incollection)
Consumer Depth Cameras for Computer Vision - Research Topics and Applications
Fossati, A., Gall, J., Grabner, H., Ren, X., Konolige, K.
Advances in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Springer, 2012 (book)
2011
Steerable random fields for image restoration and inpainting
Roth, S., Black, M. J.
In Markov Random Fields for Vision and Image Processing, pages: 377-387, (Editors: Blake, A. and Kohli, P. and Rother, C.), MIT Press, 2011 (incollection)
Benchmark datasets for pose estimation and tracking
Andriluka, M., Sigal, L., Black, M. J.
In Visual Analysis of Humans: Looking at People, pages: 253-274, (Editors: Moesland and Hilton and Kr"uger and Sigal), Springer-Verlag, London, 2011 (incollection)
Fields of experts
Roth, S., Black, M. J.
In Markov Random Fields for Vision and Image Processing, pages: 297-310, (Editors: Blake, A. and Kohli, P. and Rother, C.), MIT Press, 2011 (incollection)
Model-Based Pose Estimation
Pons-Moll, G., Rosenhahn, B.
In Visual Analysis of Humans: Looking at People, pages: 139-170, 9, (Editors: T. Moeslund, A. Hilton, V. Krueger, L. Sigal), Springer, 2011 (inbook)
2009
An introduction to Kernel Learning Algorithms
Visual Object Discovery
Sinha, P., Balas, B., Ostrovsky, Y., Wulff, J.
In Object Categorization: Computer and Human Vision Perspectives, pages: 301-323, (Editors: S. J. Dickinson, A. Leonardis, B. Schiele, M.J. Tarr), Cambridge University Press, 2009 (inbook)
2008
GNU Octave Manual Version 3
John W. Eaton, David Bateman, Soren Hauberg
Network Theory Ltd., October 2008 (book)
2007
Probabilistically modeling and decoding neural population activity in motor cortex
Black, M. J., Donoghue, J. P.
In Toward Brain-Computer Interfacing, pages: 147-159, (Editors: Dornhege, G. and del R. Millan, J. and Hinterberger, T. and McFarland, D. and Muller, K.-R.), MIT Press, London, 2007 (incollection)
2006
Products of “Edge-perts”
Gehler, P., Welling, M.
In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 18, pages: 419-426, (Editors: Weiss, Y. and Sch"olkopf, B. and Platt, J.), MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 2006 (incollection)
2005
Visual motion analysis method for detecting arbitrary numbers of moving objects in image sequences
Jepson, A. D., Fleet, D. J., Black, M. J.
US Pat. 6,954,544, October 2005 (patent)
A Flow-Based Approach to Vehicle Detection and Background Mosaicking in Airborne Video
2004
Development of neural motor prostheses for humans
Donoghue, J., Nurmikko, A., Friehs, G., Black, M.
In Advances in Clinical Neurophysiology, (Editors: Hallett, M. and Phillips, L.H. and Schomer, D.L. and Massey, J.M.), Supplements to Clinical Neurophysiology Vol. 57, 2004 (incollection)
2003
Method and apparatus for generating a condensed version of a video sequence including desired affordances
Black, M. J., Ju, S., Minneman, S., Kimber, D.
US Pat. 6,560,281, May 2003 (patent)
Apparatus and method for identifying and tracking objects with view-based representations
Black, M. J., Jepson, A.
US Pat. 6,526,156, February 2003 (patent)
2002
Bayesian Inference of Visual Motion Boundaries
Fleet, D. J., Black, M. J., Nestares, O.
In Exploring Artificial Intelligence in the New Millennium, pages: 139-174, (Editors: Lakemeyer, G. and Nebel, B.), Morgan Kaufmann Pub., July 2002 (incollection)
1999
Artscience Sciencart
Black, M. J., Levy, D., PamelaZ,
In Art and Innovation: The Xerox PARC Artist-in-Residence Program, pages: 244-300, (Editors: Harris, C.), MIT-Press, 1999 (incollection)
1998
Looking at people in action - An overview
Yacoob, Y., Davis, L. S., Black, M., Gavrila, D., Horprasert, T., Morimoto, C.
In Computer Vision for Human–Machine Interaction, (Editors: R. Cipolla and A. Pentland), Cambridge University Press, 1998 (incollection)
1997
Recognizing human motion using parameterized models of optical flow
Black, M. J., Yacoob, Y., Ju, X. S.
In Motion-Based Recognition, pages: 245-269, (Editors: Mubarak Shah and Ramesh Jain,), Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, MA, 1997 (incollection)
1995
Apparatus and method for tracking facial motion through a sequence of images
Black, M. J., Yacoob, Y.
US Pat. 5,802,220, December 1995 (patent)
Apparatus and method for recognizing facial expressions and facial gestures in a sequence of images
Black, M. J., Yacoob, Y.
US Pat. 5,774,591, December 1995 (patent)
Image segmentation using robust mixture models
Black, M. J., Jepson, A. D.
US Pat. 5,802,203, June 1995 (patent)
1993
Mixture models for optical flow computation
Jepson, A., Black, M.
In Partitioning Data Sets, DIMACS Workshop, pages: 271-286, (Editors: Ingemar Cox, Pierre Hansen, and Bela Julesz), AMS Pub, Providence, RI., April 1993 (incollection)